Lithium-ion batteries are more widely available at a lower price. This may be a factor when considering the overall cost of a 24V 150AH battery. Market reflects that lithium polymer battery production and technology is still maturing and that their cycle life continues to improve.
Part1: Processes of 24V 150AH Lithium Battery assembly:
- Initial State of Battery Cells: 24V 150AH Lithium Battery begins with a set of eight individual lithium-ion battery cells. These cells have varying voltage levels, ranging from 3.05V to 3.36V. This makes them unsuitable for building a functional battery pack without further preparation.
- Cell Balancing Process: The presenter demonstrates a manual method to balance the voltage and internal resistance (IR) of the cells. They connect all the negative terminals of the eight cells together using a wire and then do the same for the positive terminals. This parallel connection is maintained for approximately 48 hours.
- Post-Balancing Voltage Check: After 48 hours of being connected in parallel, the presenter disconnects the cells and checks their voltage using a multimeter. All eight cells now exhibit remarkably consistent voltage readings of approximately 3.295-3.296V, indicating a successful balancing process.
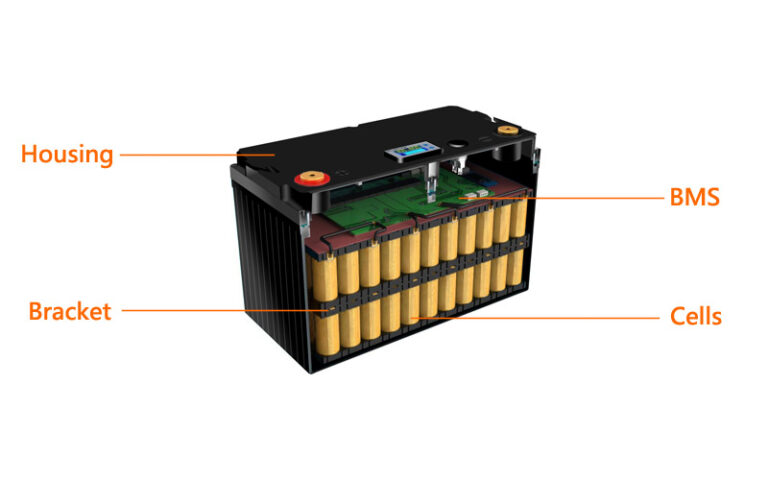
- Battery Pack Assembly: The presenter notes that now the cells are perfectly balanced, they are ready to be assembled into a 24V 150Ah battery pack. The recommendation is to use an 8s 100A BMS (Battery Management System) for this purpose.
- Discussion of Lithium Battery Production: the presenter is working on a video series, providing information on how to build Li-ion batteries and also on the potential pitfalls in the process. They also mention that their company, Maxmol, will be releasing batteries in the near future. They also plug their app that sells components related to Li-ion battery building.
- Lithium-ion vs. Lithium-polymer Batteries: Lithium-ion ( Li-ion ) VS LiPo discusses the differences between lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries. Lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolyte while lithium-polymers use a microporous electrolyte. Lithium-ion batteries, generally cylindrical or rectangular, are more rigid due to their construction while lithium polymer batteries have more flexible designs, using aluminum plastic composite as a packing material.
- Performance Characteristics: Both types of batteries are capable of high power output. Lithium-ion batteries are typically cheaper and have longer lives (2-3+ years and 300-500 cycles), while lithium-polymer batteries are gaining popularity due to flexible design and safety factors. The presenter, from the company Grapeville, believes that lithium-polymer batteries will be more sought after in the future.
Part2: General Specifications
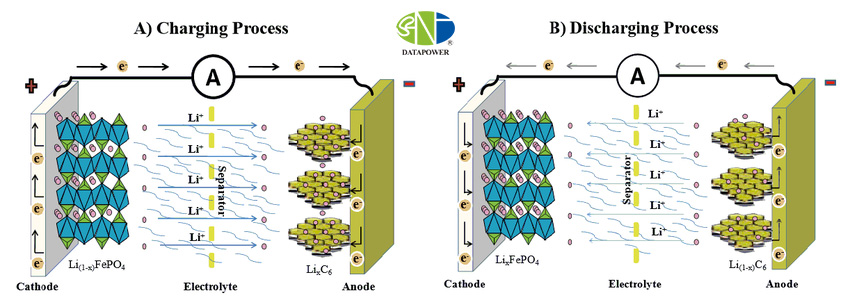
The battery pack uses Lithium Iron-Phosphate (LiFePO4) chemistry, which is considered ultra-safe with no risk of thermal runaway, fire, or explosion.It has a high service life of 3000 cycles and more.It allows deep discharge up to 100%. The battery has an embedded Battery Management System (BMS) to improve lifespan and secure the battery.
It contains no lead, rare earths, acid, or degassing.It has a calendar life of over 10 years.It has excellent temperature robustness, operating from -20 °C up to +60 °C.It can be deployed flexibly, with up to 16 packs in parallel and 2 in series.The battery provides constant power during discharge due to very low internal resistance.It has very low Peukert’s losses with an energy efficiency >98 %.Self-discharge is very low, at less than 3 % per month.There is no memory effect.It is about 50 % lighter and 40% smaller than equivalent Lead-AGM batteries with the same usable energy.
Electrical Specifications:
- Nominal voltage is 25.6V and nominal capacity is 150Ah, with a stored energy of 3.840 kWh.
- Volumetric energy density is 148.2 Wh/L, and specific energy is 120.0 Wh/Kg.
- Internal resistance is ≤ 50mΩ.Energy efficiency is > 98%.
- Standard charge voltage is 28.8 V ± 0.4 V (with an optional floating voltage of 26.72V max).
- The battery uses a CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage) charge mode.Continuous charge current is 100 A, with a maximum charge current of 150 A
- The BMS charge cut-off voltage is 29.6 V ± 0.1V.Instant peak discharge current is 550 A ± 50 A (max 300mS).Continuous discharge current is 120 A (3.07 kW).
- Maximum discharge current (for < 30s) is 180 A (4.61 kW).
- The BMS discharge cut-off voltage is 20 V.
Environmental and Mechanical Specifications:
- Charge temperature range is 0°C to +60°C
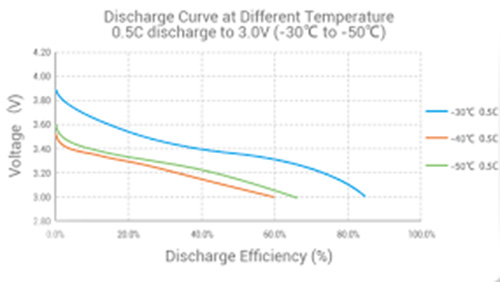
- discharge temperature range is -20°C to +60°C.
- Storage temperature is 0°C to +50°C with 60±25% relative humidity.
- The battery has an IP protection level of IP 65.
- The cells are cylindrical, with an ABS casing material.Dimensions are L: 500mm (520mm) x W: 239mm x H: 217 mm.
Applications:
The battery is designed for use in a variety of applications such as electrical vehicles, robotics, solar and wind energy storage, marine, street lighting, CCTV, UPS, telecom, and medical equipment1.

Part3: Lithium Battery Structure and Main Lithium Battery Types
- Why is it crucial to balance lithium battery cells before assembling a battery pack, and how can it be done without specialized equipment?
Balancing cells is crucial because individual cells within a battery pack can have slightly different voltage levels. If these differences aren’t addressed, the cells with the lowest voltage will be stressed the most during charging, leading to premature failure, reduced capacity, and poor overall battery performance. Without specialized equipment, you can balance cells by connecting all the positive terminals together and all the negative terminals together. This allows the cells to equalize their voltage over a period. After this time, each individual cell’s voltage should be very similar. - What is a BMS, and why is it necessary when building a lithium battery?A Battery Management System (BMS) is an essential component when building lithium batteries. It protects the cells by preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. Additionally, a BMS can monitor cell voltage, temperature, and current, ensuring the overall safety and longevity of the battery pack. This battery using an 8s 100A BMS for an 8 cell 24V system.
- What are the primary differences between Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries?
Li-ion batteries use a liquid chemical electrolyte and typically come in cylindrical or rectangular shapes. LiPo batteries, on the other hand, use a micro porous electrolyte and a flexible aluminum plastic composite film. This allows LiPo batteries to be lighter, more flexible, and produced in a variety of shapes (ultra-thin, curved, etc.) that better fit modern devices. - Which type of lithium battery, Li-ion or LiPo, is more likely to experience thermal runaway, and why?
While both types of lithium batteries are susceptible to thermal runaway, LiPo batteries are generally considered to have a lower chance due to their construction. Li-ion batteries require a rigid case to press electrodes together, whereas LiPo batteries are more flexible and use an aluminum film for casing, which provides better containment and reduced risk of electrolyte leakage and related safety issues, making them more resistant to thermal runaway.